What Is A Cistern Used For

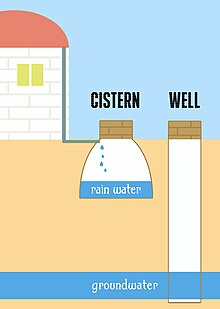
The departure between a cistern and a well is in the source of the water: a cistern collects rainwater where a well draws from groundwater.
A cistern (Middle English cisterne , from Latin cisterna , from cista , "box", from Greek κίστη kistē , "basket")[1] is a waterproof receptacle for holding liquids, usually h2o. Cisterns are oft built to catch and store rainwater.[2] Cisterns are distinguished from wells by their waterproof linings. Modernistic cisterns range in capacity from a few litres to thousands of cubic metres, effectively forming covered reservoirs.[ citation needed ] [3]
Origins [edit]
Early domestic and agricultural apply [edit]

Waterproof lime plaster cisterns in the floors of houses are features of Neolithic village sites of the Levant at, for instance, Ramad and Lebwe,[four] and by the late quaternary millennium BC, as at Jawa in northeastern Lebanon, cisterns are essential elements of emerging h2o management techniques in dry-land farming communities.[5]
The Ancient Roman impluvium, a standard characteristic of the domus house, by and large had a cistern underneath. The impluvium and associated structures collected, filtered, cooled, and stored the water, and also cooled and ventilated the firm.
Castle cisterns [edit]

In the Centre Ages, cisterns were often constructed in colina castles in Europe, especially where wells could not be dug securely enough. There were two types: the tank cistern and the filter cistern. Such a filter cistern was built at the Riegersburg in Austrian Styria, where a cistern was hewn out of the lava rock. Rain water passed through a sand filter and collected in the cistern. The filter cleaned the rain water and enriched it with minerals.[ citation needed ]
Present-mean solar day use [edit]

Cisterns are ordinarily prevalent in areas where water is deficient, either because it is rare or has been depleted due to heavy use. Historically, the h2o was used for many purposes including cooking, irrigation, and washing.[6] Nowadays-twenty-four hours cisterns are often used only for irrigation due to concerns over water quality. Cisterns today can besides be outfitted with filters or other water purification methods when the water is intended for consumption. It is not uncommon for a cistern to exist open in some manner in order to grab pelting or to include more elaborate rainwater harvesting systems. It is important in these cases to have a system that does non go out the water open up to algae or to mosquitoes, which are attracted to the h2o and then potentially carry disease to nearby humans.[7]
Some cisterns sit on the summit of houses or on the basis higher than the house, and supply the running water needs for the firm. They are frequently supplied by wells with electric pumps, or are filled manually or past truck delivery, rather than by rainwater collection. Very mutual throughout Brazil, for case, they were traditionally made of concrete walls (much similar the houses themselves), with a similar concrete tiptop (almost 5 cm/2 inches thick), with a piece that can exist removed for water filling and then reinserted to proceed out debris and insects. Modernistic cisterns are manufactured out of plastic (in Brazil with a characteristic bright blue color, round, in capacities of nigh x,000 and fifty,000 liters (2641 and 13,208 gallons)). These cisterns differ from water tanks in the sense that they are not entirely enclosed and sealed with one class, rather they have a lid fabricated of the aforementioned fabric as the cistern, which is removable by the user.[ commendation needed ]
To go on a clean h2o supply, the cistern must be kept clean. Information technology is of import to inspect them regularly, keep them well enclosed, and to occasionally empty and clean them with a proper dilution of chlorine and to rinse them well. Well water must exist inspected for contaminants coming from the basis source. City water has up to 1ppm (parts per million) chlorine added to the water to keep it clean, and in many areas can be ordered to exist delivered straight to the cistern by truck (a typical price in Brazil is BRL$l, US$20 for 10,000 liters). If at that place is any question about the water supply at any point (source to tap), and then the cistern water should not be used for drinking or cooking. If information technology is of acceptable quality and consistency, then it can be used for (one) toilets, and housecleaning; (ii) showers and handwashing; (3) washing dishes, with proper sanitation methods,[eight] and for the highest quality, (4) cooking and drinking. Water of non-acceptable quality for the same uses may notwithstanding be used for irrigation. If it is free of particulates but not low enough in bacteria, then boiling may also exist an constructive method to prepare the h2o for drinking.[ citation needed ]

Bermuda's white-stepped roofs for collecting rainwater channeled into cisterns
Many greenhouses rely on a cistern to help meet their water needs, peculiarly in the United States. Some countries or regions, such equally Flanders, Bermuda and the U.Southward. Virgin Islands, have strict laws requiring that rainwater harvesting systems be built alongside any new construction, and cisterns can exist used in these cases. In Bermuda, for example, its familiar white-stepped roofs seen on houses are part of the rainwater collection organization, where water is channeled past roof gutters to below-ground cisterns.[nine] Other countries, such as Nippon, Federal republic of germany, and Kingdom of spain, besides offer financial incentives or taxation credit for installing cisterns.[10] Cisterns may also be used to store water for firefighting in areas where there is an inadequate water supply. The metropolis of San Francisco, notably, maintains burn down cisterns under its streets in case the principal water supply is disrupted. In many apartment areas the apply of cisterns is encouraged to absorb excess rainwater which otherwise tin can overload sewage or drainage systems by heavy rains (certainly in urban areas where a lot of footing is surfaced and doesn't allow the ground absorb water).[ commendation needed ]
Bathing [edit]
In some southeast Asian countries such every bit Malaysia and Indonesia showers are traditionally taken by pouring h2o over one's body with a dipper (this practice comes from before piped water was common). Many bathrooms even in modern houses are constructed with a minor cistern to hold water for bathing by this method.[ citation needed ]
Toilet cisterns [edit]
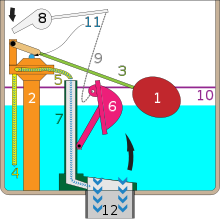
A traditional gravity toilet tank last the affluent wheel.
1. float, 2. fill up valve, 3. lift arm, 4. tank fill tube, five. bowl fill tube, vi. flush valve flapper, 7. overflow tube, eight. affluent handle, ix. chain, 10. make full line, 11. fill valve shaft, 12. flush tube
The modern water cupboard (WC) or toilet utilises a cistern to reserve and hold the correct amount of water required to flush the toilet bowl. In earlier toilets, the cistern was located loftier above the toilet basin and connected to it by a long pipe. It was necessary to pull a hanging concatenation connected to a release valve located inside the cistern in order to flush the toilet. Modern toilets may exist shut coupled, with the cistern mounted straight on the toilet basin and no intermediate pipe. In this arrangement, the flush mechanism (lever or push button) is usually mounted on the cistern. Concealed cistern toilets, where the cistern is built into the wall behind the toilet, are also available. A flushing trough is a type of cistern used to serve more than than ane WC pan at one time. These cisterns are becoming less mutual nevertheless. The cistern was the genesis of the modern bidet.[ citation needed ]
At the beginning of the flush cycle, as the h2o level in the toilet cistern tank drops, the affluent valve flapper falls back to the lesser, stopping the main period to the flush tube. Considering the tank h2o level has yet to attain the make full line, water continues to flow from the tank and bowl fill tubes. When the h2o again reaches the fill line, the float volition release the fill valve shaft and water flow will stop.
I One thousand thousand Cisterns Plan [edit]
In northeastern Brazil, the Ane Million Cisterns Program (Programa 1 Milhão de Cisternas or P1MC) has assisted local people with water management. The Brazilian government adopted this new policy of rainwater harvesting in 2013.[11] The Semi-Arid Joint (ASA) has been providing managerial and technological support to establish cement-layered containers, called cisterns, to harvest and store rainwater for small farm-holders in 34 territories of 9 states where ASA operates (MG, BA, SE, AL, PE, PB, RN, CE and PI).[12]
The rainwater falling on the rooftops are passed through pipelines or gutters and stored in the cistern.[thirteen] The cistern is covered with a lid to avoid evaporation. Each cistern has a capacity of 16,000 liters. Water collected in it during 3–4 months of the rainy season can sustain the requirement for drinking, cooking, and other basic sanitation purposes for rest of the dry periods. Past 2016, 1.2 million RWH cisterns were implemented for human consumption lonely.[14] After positive results of P1MC, the government introduced some other plan named "1 State, Two H2o Programme" (Uma Terra, Duas Águas, P1 + 2), which provides a farmer with some other slab cistern to support agronomical production.[15]
Notable examples [edit]

- Basilica Cistern in Istanbul, Turkey
- Aljibe of the Palacio de las Veletas in Cáceres, Espana
- Portuguese cistern (Mazagan) in El Jadida, Morocco
- Cistern in Silves, Portugal
- Matera, southern Italy
- Asa of Judah had congenital a cistern, and the prophet Jeremiah was later on thrown in it later on prophesying the Babylonian invasion
- Cistern in Genesis 37:20, 22
See as well [edit]
- Ab anbar, Western farsi cistern
- List of Roman cisterns
- Stepwell
- Taanka
- Water tank
Gallery [edit]
-

Plastic cistern
-

-
-

-

Sign indicating a cistern in Japan
References [edit]
- ^ Webster'southward Ninth New Collegiate Dictionary, 1990 edition, etymology of "cistern".
- ^ "Cisterns".
- ^ "Cistern Design" (PDF). North Carolina Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services . Retrieved 2020-04-13 .
- ^ Robert Miller, "Water employ in Syria and Palestine from the Neolithic to the Statuary Age", World Archæology, two.3 (February 1980:331-341) p. 334.
- ^ Roberts, N. (1977). "Water conservation in ancient Arabia". Proceedings of the Seminar for Arabian Studies. seven: 134–46.
- ^ Mays, Larry; Antoniou, George; Angelakis, Andreas (2013). "History of Water Cisterns: Legacies and Lessons" (PDF). Water. five (four): 1916–1940. doi:10.3390/w5041916.
- ^ al-Kibsi, Huda (2007-09-29). "Republic of yemen takes some other wait at cisterns". Yemen Observer. Archived from the original on 2012-02-08. Retrieved 2020-05-11 .
- ^ "Naturnaher Umgang mit Regenwasser" (PDF). Bayerisches Landesamt für Umwelt LfU (in German). Retrieved 2020-04-12 .
- ^ Low, Harry (23 December 2016). "Why houses in Bermuda have white stepped roofs". BBC News . Retrieved 30 August 2019.
- ^ Scheidewig. "Geld sparen durch Zisternennutzung". Garten-Zisternen (in German language). Retrieved 2020-04-13 .
- ^ Lindoso, D.P.; Eiró, F.; Bursztyn, Grand.; Rodrigues-Filho, S.; Nasuti, S. (2018). "Harvesting water for living with drought: Insights from the Brazilian human coexistence with semi-aridity approach towards achieving the Sustainable Evolution Goals". Sustainability. x (three): 622. doi:x.3390/su10030622.
- ^ Pragana, Verônica (2017-12-29). "Acesso à água para produção é ampliado para mais de 6,8 mil famílias do Semiárido". IRPAA - Instituto Regional da Pequena Agropecuária Apropriada.
- ^ Lindoso, D.P.; Eiró, F.; Bursztyn, Grand.; Rodrigues-Filho, S.; Nasuti, Southward. (2018). "Harvesting water for living with drought: Insights from the Brazilian human coexistence with semi-aridity approach towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals". Sustainability. 10 (3): 622. doi:10.3390/su10030622.
- ^ "Programa Cisternas democratiza acesso à água no Semiárido". Government of Brazil. 2016.
- ^ Lindoso, D.P.; Eiró, F.; Bursztyn, M.; Rodrigues-Filho, S.; Nasuti, S. (2018). "Harvesting h2o for living with drought: Insights from the Brazilian human coexistence with semi-aridity approach towards achieving the Sustainable Development Goals". Sustainability. 10 (three): 622. doi:ten.3390/su10030622.
External links [edit]
![]()
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Cisterns.
- Old House Web - Celebrated Water Conservation.
What Is A Cistern Used For,
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cistern
Posted by: hamptonacantiming.blogspot.com



0 Response to "What Is A Cistern Used For"
Post a Comment